Generic PCBs
There are some generic PCBs which are used for different devices. The goal is to reuse few PCB types many times instead of developing special ones for each device.
Here are the specs for the PCBs:
| Generic Maxi Speed | Generic Maxi | Generic Midi | Generic Micro | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
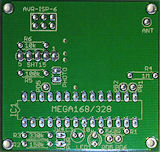
| Purpose | This board has dual voltage support and an optional crystal to make it possible to run the microcontroller at its full speed of 20 MHz. Full description | This board offers the maximum amount of connections. It can be used as experimental board or for a device with many functions. | This board offers a mediocre amount of connections with a reasonable small size. No SMD-soldering is needed (except the RFM12 mounting). | This SMD PCB can be integrated in e.g. existing home appliances because of the small form factor. Experience in soldering is needed. |
| Sample Appliances |
|
|
|
|
| Picture | 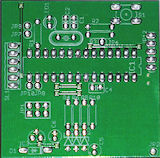 |
 |
 |
 |
| Size | 50 x 50 mm (25 cm²) 2 x 2 in (4 in²) | 76 x 48 mm (36.5 cm²) 2.1 x 1.9 in (5.7 in²) | 48 x 45 mm (21.6 cm²) 1.9 x 1.8 in (3.3 in²) | 35 x 30 mm (10.5 cm²) 1.4 x 1.2 in (1.6 in²) |
| Type | conventional THTThrough hole technology This is the conventional technique to stick pins of components through the PCB and solder them. This is easy to build up, unlinke using SMD components. | conventional THT | conventional THT | SMDSurface-mounted device Using this technique, the components are soldered directly to the surface of the PCB. The components are often very small. Their pin pitch is also small. Building up these devices needs some experience in soldering. |
| Clock Source | optional crystal | optional crystal | internal RC oscillator only | internal RC oscillator only |
| I/O Pins | 8 | 14 | 8 | 8 |
| Assembly Options | Crystal, voltage measurement, reset button and others | Crystal | Voltage measurement | 3.3V voltage regulator for both ATMega and RFM12 |
| Links | Schematics + Layout at Codeberg | Schematics + Layout at Codeberg | Schematics + Layout at Codeberg | Schematics + Layout at Codeberg |


